The Global View and the Future View
|
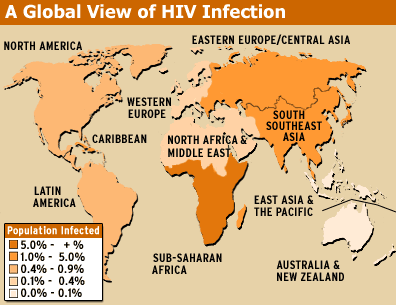
Posted By: Tawain Kelly on March 25, 2006 If we do nothing this is the Future of HIV/AIDS CURRENT REGIONAL ANALYSIS Sub-Saharan Africa: Sub-Saharan Africa makes up 10% of the world’s population and more than 60% of the worlds HIV/AIDS population. It is, by far, the region most affected by the virus, with a prevalence rate of 7.4% (an estimated 25 million people infected) and 12 million children orphaned because of the disease. For the better part of the 20th century, the region had been making efforts to increase the life expectancy of its population but HIV/AIDS has created a new cause of early death that has essentially erased all of the progress that had previously been made. Because of the virus, today the life expectancy for someone living in the region is only 47 years. However, the AIDS epidemic within the region varies and it is impossible to talk of a single “African” epidemic. For example, while HIV prevalence rates in West and Central Africa have stayed around 5% or below, South Africa has an alarming prevalence rate of 21.5%. The prevalence rates are also much higher in refugee populations. Certain trends are prevalent throughout the whole region. For example, on average women are more affected than men because of problems such as sexual abuse and exploitation. UNAIDS writes, “Recent population-based studies suggest that there are on average 36 young women living with HIV for every 10 young men in sub-Saharan Africa.” Also, racism and social class have played a large role in HIV/AIDS prevalence rates. The disease has disproportionately affected poor, black Africans and homosexual men of all classes causing stigmas and stereotypes. Latin America: It is estimated that 600 to 700 people from Latin America and the Caribbean are infected daily with HIV. Therefore, HIV/AIDS in Latin America is a major concern. The HIV prevalence rate is at 0.6% and it is believed that more than 1.7 million people in the region are infected with the virus. Of these cases, Brazil accounts for one-third of them. Although the epidemic started mainly in populations of men having sex with men and injection drug users, today the virus is transmitted much more through heterosexual contact. The epidemic within Latin America is diverse, but certain factors are prevalent throughout the region. For example, the Roman Catholic Church’s stance against condom use has meant that many are not educated about safe sex. Despite these challenges, Latin America has been a leader in providing antiretroviral therapy to all PLWHAs. Brazil has done an especially remarkable job at making treatment facilities available. Middle East and North Africa: In most nations of the Middle East and North Africa (except for the Sudan), the HIV/AIDS epidemic is still in its early stages. This means that if effective prevention methods are implemented, these countries might be able to halt the spread of the virus. However, countries like Libya and Iran must work fast because the virus is spreading faster there. Overall, the HIV prevalence rate in the region is 0.3% and it is estimated that 540,000 people are infected. HIV is being transmitted through diverse means, but the sex industry, men who have sex with men, and injection drug use are some of the more prevalent transmission methods. South and Southeast Asia: This extremely large region has several HIV/AIDS epidemics occurring within it. Overall, the total number of HIV infections and annual AIDS deaths is higher than in any other region, except for sub-Saharan Africa. The average HIV prevalence rate for the area is 0.6%, and it is believed that there are 7,100,000 people infected. However, the region is very diverse in terms of the effect that the virus has had. Some countries were hit early, such as Myanmar, Cambodia, and Thailand, and thus have experienced very devastating epidemics. Others, such as Indonesia and Vietnam, are only now starting to see the rapid growth of the epidemic. In a nation of more than 1 billion people, India by far has the greatest infection rates, with 5.1 million people infected. East Asia: Comprised of primarily China, Japan, North Korea, and South Korea, East Asia has a very low infection rate compared with other continents. The HIV prevalence rate in the region is 0.1%, and there are an estimated 1.1 million people living with HIV in the area. Because of its size, the region is dominated by China, a country in which HIV has a firm presence because of injection-drug use and the sex industry. There has been a high rate of HIV transmission from blood transfusions as well, especially in rural areas. While infection rates in other areas of East Asia are considerably lower, there is a fear that without better education, the epidemic will continue to grow. Eastern Europe and Central Asia: The number of people infected with HIV in Eastern Europe and Central Asia has risen dramatically in the past ten years; today it is estimated that 1.4 million people are infected. The overall HIV prevalence rate is 0.8%, with the most serious epidemic located in the Ukraine, where there has been a surge of new cases. However, the largest epidemic remains in the Russian Federation. Evidence suggests that the virus is in its early stages in several central Asian and Caucasian Republics too. While the region’s epidemics are diverse, there are a few common features. For the most part, the epidemics in the area are in their early stages, meaning that effective prevention might slow the spread of the virus. Also, HIV is infecting mostly young people in the region, with 80% of all cases occurring in people under 30. Last, transmission through heterosexual contact is on the rise throughout Eastern Europe and Central Asia, suggesting that the virus will infect a wider range of people. North America: The HIV/AIDS epidemic in the United States has changed dramatically over the past 10 years. While it started as a disease that mainly affected white men who were having sex with men, now the virus is disproportionately infecting African-Americans, and an increasing number of women. For example, while African-Americans are only 12% of the population, they account for more than 50% of all new infections. Latinos make up another 20% of new infections, although they account for only 14% of the population. While race is not a risk factor, poverty and socioeconomic deprivation definitely are factors. A correlation can be seen between high prevalence rates and low-income levels. The HIV prevalence rate in the United States is 0.6% and it is estimated that 1.0 million people are infected. The main method of transmission is still men having sex with men, although transmission through heterosexual contact is increasing. Western Europe: In Western Europe, thousands of new infections are occurring each year. Many of those infected are unaware of their status because it is a common misconception that HIV/AIDS is no longer a major concern, so people do not regularly get tested. For example, it is believe that one-third of those infected in the U.K. are unaware that they are HIV-positive. The HIV prevalence rate in Western Europe is 0.3% and it is estimated that 570,000 people are infected. Many of the new HIV cases are from people that originated in countries with large epidemics. Luckily though, Western Europe has successfully made antiretroviral therapy available to those in need. Because of this, AIDS-related deaths remain relatively low. While men having sex with men are still the most common mode of transmission, heterosexual transmission is on the rise. In fact, 1997 to 2002 saw a 122% increase in this form of transmission. FUTURE PROJECTIONS Sub-Saharan Africa: In 2004 alone, AIDS was responsible for 2.3 million deaths in sub-Saharan Africa. This number will continue to rise if broad access to antiretroviral therapy is not made available to the population at large. In fact, if current trends continue, it is estimated that the populations of five African nations (Botswana, Mozambique, Lesotho, Swaziland, and South Africa) will begin to shrink because of the virus. Thus, HIV/AIDS will continue to have a greater and greater impact on the region if treatment options and prevention initiatives do not become available. Latin America: Because of the progress made with making antiretroviral treatment available, AIDS mortality rates have declined in many Latin American countries. However, more needs to be done on the prevention front to stop the spread of the virus. Middle East and North Africa: Because of the region’s lack of willingness to openly discuss HIV/AIDS and to offer HIV education programs and initiatives, there is an increased risk that the virus will continue to spread to wider sectors of society. Although the spread of the virus is still in its early stages, without effective prevention methods the prevalence rate will continue to rise. Many countries in the area have been slow to react to the virus, and have not implemented programs such as “condom promotion.” Without programs aimed at educating the public and decreasing social stigma, the virus will spread in the region. South and Southeast Asia: The region of South and Southeast Asia has been somewhat dominated by the epidemic in India. Currently, more than 5 million people are infected in India and the Central Intelligence Agency’s National Intelligence Council predicts that 20 million to25 million Indians will be infected by 2010, more than any other country in the world. Although treatment and prevention initiatives are available in India, its enormous population means that even more must be done to stop the spread of the disease. East Asia: The prevalence rate of HIV in the region has been relatively low and has remained mainly a problem among certain vulnerable populations. However, if the governments of the region do not begin to make genuine efforts at prevention, the virus will spread to the general population. The director of UNAIDS, Dr. Peter Piot, stated, “Low condom use, limited access to HIV testing, gender inequality, widespread injecting drug use and sex work are a dangerous cocktail that could provoke a rapid expansion of the epidemic. If HIV prevention programs are urgently scaled-up, 6 million HIV infections could be prevented in the next five years in the region. If Asian countries do not rise up to the challenge, then 12 million people will become newly infected.” Eastern Europe and Central Asia: Although the epidemic is in its early stages in the region, HIV is, unfortunately, on the rise. A relatively new phenomenon, injection drug use is becoming an increasingly large problem in the region that has led to many new HIV cases in countries such as Russia and the Ukraine. Without effective prevention efforts, the combination of drug use and increased high-risk sexual behavior means it is estimated that HIV prevalence rates will rise in the region. North America: More needs to be done in terms of prevention efforts to ensure that the virus does not continue to spread in North America. Western Europe: With its older and more entrenched epidemic, Europe has had more time than other regions to confront the HIV/AIDS epidemic. As a result, antiretroviral therapy is widely available to all who require it. Although treatment is available, prevention strategies have been faltering and many estimate that Europe should brace itself for a larger epidemic. Countries in the region seem to have let down their guard about prevention, and thus have reported an increase in high-risk sexual behavior (such as less frequent condom use). Without more effective prevention methods, the amount of HIV/AIDS in the region is sure to rise. If you enjoyed this article, Join HBCU CONNECT today for similar content and opportunities via email! |
Comments
More From This Author
Latest Blogs
 |
WOMEN OF GOD in UNITY Working Together5 Anointed Christian Women talking about things happening in our communities Throughout the nation and should be change with our help daily. And there will be 2 recording gospel Artist at this event p ...more
Min Sammy Jackson • 52 Views • March 9th, 2026 |
 |
WOMEN OF GOD in UNITY Working Together5 Anointed Christian Women talking about things happening in our communities Throughout the nation and should be change with our help daily. And there will be 2 recording gospel Artist at this event p ...more
Min Sammy Jackson • 45 Views • March 9th, 2026 |
 |
Behind the Wheel of the Hot 2026 Kia Sportage ReviewCompact SUVs remain competitive, and Kia’s best-selling model for 2026, the Sportage, gets a major mid-cycle update to stay ahead. During a week with the new Sportage Hybrid SX-Prestige AWD, I tested ...more
Randi Payton • 162 Views • March 5th, 2026 |
 |
Season OpenerOpen door looks inviting; You see noone near the vehicle yet the door has been wide open for an unusual amount of time!
🤔💭“maybe I should help them out or should I just stick to th ...more
How May I Help You NC • 170 Views • March 4th, 2026 |
 |
Motivational Artist MARCUS PARKER Creates Rize Mode A AI Powered Artist@MARCUSPARKER #MARCUSPARKER
@RIZEMODE #RIZEMODE
@WISEDIVAS #WISEDIVAS
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Underground Motivator MARCUS PARKER Launches AI Artists and New Guide to Help Others Build Their Own ...more
LaMarr Blackmon • 207 Views • March 2nd, 2026 |
Popular Blogs
 |
Divorce in America in 2009 – What’s love got to do, got to do with it?
Join Brother Marcus and the cast and the crew of the Brother Marcus Show live this Sunday evening on February 1, 2009 @ 8:00 p.m. for another hot topic in our community! “Divorce in America in 2009 ...more
Brother Marcus! • 70,865,781 Views • January 27th, 2009 |
 |
VISINE ALERT!!!Seemingly innocent medication such as Visine eyedrops are used by people to concoct a mixture with similar effects as a date-rape drug.
When mixed with alcohol and taken orally, the eyedrops can l ...more
Siebra Muhammad • 118,526 Views • May 23rd, 2009 |
 |
"Chain Hang Low" check out the real meaning of the Lyrics!Recently there is a new artist out of Saint Louis that goes by the name JIBBS. Jibbs debut single "Chain hang low" has a history that most people are not aware of. The particular nursery rhyme that th ...more
Tyhesha Judge-Fogle • 75,945 Views • November 9th, 2006 |
 |
HBCU Marketplace Gifts: Divine 9 Premium Fraternity / Sorority Playing CardsVendor: Charles Jones
Item Price: $20.00
Price Includes Shipping: Yes - Shipping Included
Item Description:
Pantheon Series - Divine 9 - Premium Playing Cards (choose Gold Series or Silve ...more
How May I Help You NC • 61,775 Views • December 2nd, 2018 |












